What is MSM (Methylsulfonylmethane)?
What is MSM (Methylsulfonylmethane)?
Methylsulfonylmethane, otherwise known as MSM, is a relatively common sulfur-based nutritional supplement that can help support gallbladder health and healing. It is closely related to DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide), and has in fact previously been referred to as crystalline DMSO due to the relativity of these two substances. Though available as a powder or supplement, MSM is also naturally produced in the human body, as well as in plants and other animals.
Medicinal Applications of MSM
MSM may be able to help treat the following health problems:- Arthritis
- Chronic inflammation
- Oxidative damage done by nitric oxide and other harmful ROS
- Seasonal allergies
- Rosacea, ichthyosis, scleroderma, and other skin problems
- Cancer (specifically breast cancer, colon cancer, stomach cancer, liver cancer, esophageal cancer, skin cancer, and bladder cancer)
- Chronic pain
- Constipation
- Osteoporosis
- Hair loss
- High cholesterol
- Emphysema, pneumonia, and some other lung disorders
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and other autoimmune conditions
- Type 2 diabetes
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- HIV/AIDS
- Parasite infections (Trichomonas vaginalis and Giardia in particular)
- Systemic yeast infections
- Migraines
- Radiation poisoning
- Alzheimer’s disease
- High blood pressure
- Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
- Depression/anxiety
- Diverticulosis
- Interstitial cystitis
- And more…
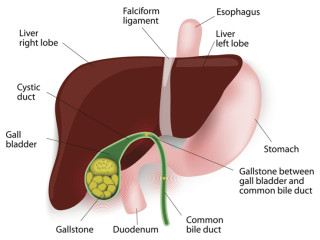
MSM is a powerful anti-inflammatory, and a large portion of popular research points to the effects of MSM on conditions involving inflammation. There are certain gallbladder conditions that involve inflammation, including cholecystitis, biliary dyskinesia, cholangitis, acalculous gallbladder disease, and others, that would specifically benefit from the anti-inflammatory qualities of MSM. Additionally, since other gallbladder issues (like gallstones, for instance) frequently either cause inflammation or pain, or both, MSM’s anti-inflammatory action can potentially help reduce pain and discomfort caused by all different kinds of gallbladder problems.
Additionally, MSM has been shown to increase glutathione production in the body. Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant that is specifically good for liver health. Detoxifying and healing the liver also directly benefits the gallbladder. Some studies have also observed that MSM can help inhibit cancer cell growth in liver cancer, in addition to preventing the metastasis of cancer cells. In terms of the gallbladder specifically, this would mean that MSM can not only help restore liver health if administered correctly and with the appropriate supportive medicines, but that it may also help prevent the cancer from spreading to the gallbladder. MSM may also be able to directly treat and/or prevent gallbladder cancer.
MSM has been studied in regard to its effect on HDL cholesterol levels, as well, with overall positive results in increasing HDL (“good”) cholesterol levels. Low HDL cholesterol (combined with high LDL cholesterol) is implicated in the development of gallbladder disease. In one study carried out over the course of 16 weeks, participants were given 3g of MSM each day. By week 8, the participants’ HDL cholesterol levels had increased somewhat, and by week 16, these levels had nearly doubled what they were in week 8.
Another Way to Look at MSM Supplementation: Sulfur Deficiency and Disease
MSM is a sulfur-based compound (methylsulfonylmethane). What this means is that it contains sulfur, an important mineral necessary for human survival, as a part of its chemical structure. Sulfur deficiency can be treated by eating foods rich in actual sulfur, such as Brussels sprouts, cabbage, garlic, onion, and others, it can be treated in some cases with sulfur-containing amino acids like cysteine (and N-acetylcysteine/NAC), methionine, and taurine, or it can be treated using sulfur-based medicinals like MSM.
 NOW Supplements, L-Cysteine 500 mg with Vitamins B-6 and C, Structural Support*, 100 Tablets
NOW Supplements, L-Cysteine 500 mg with Vitamins B-6 and C, Structural Support*, 100 Tablets
- Acne
- Arthritis
- Brittle hair and nails
- Skin problems and disorders
- Migraines
- Memory loss
- Slow wound healing
- Gastrointestinal issues
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Depression
- Skeletal disorders
- Chronic inflammation and pain
- Insulin resistance
- And more…
Sulfur is the 8th most common mineral in the body, making it an extremely important mineral when it comes to the health of the entire body. It plays a vital role in skin, muscle, and skeletal health, and is responsible for maintaining the elasticity of the skin and the bonding and coordination between the muscles, skin, and bones. When sulfur is in low supply, these areas of the body tend to suffer the most. However, other areas of the body, including the liver and gallbladder, also suffer from sulfur deficiency.
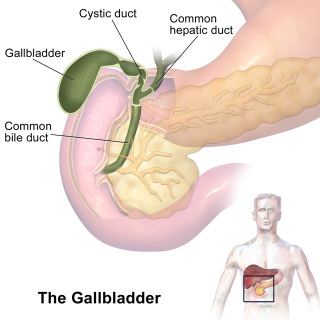
The connection between sulfur deficiency and gallbladder health originates in the liver. The liver is responsible for synthesizing cholesterol, as well as cholesterol sulfate, a water-soluble compound that plays a role in fat digestion, glucose metabolism, and insulin secretion. When a person gets enough sulfur (either through diet or supplementation), the liver will be able to produce cholesterol sulfate, which will then be passed onto the gallbladder where it is combined with bile acids. The bile acids are then released into the duodenum to digest fats (without the ability to digest fats effectively, note that other deficiencies may subsequently develop, therefore also leading to gallbladder problems).
If a person doesn’t eat enough fat or sulfur, the amount of cholesterol sulfate produced by the liver and passed into the gallbladder and intestines via bile salts will be dramatically reduced.
Cholesterol sulfate is also an important part of the barrier on the skin that protects humans from infectious pathogens or fungal disease. The conclusion can be drawn that cholesterol sulfate may play a similar role in the intestines and throughout the rest of the body (as a water-soluble molecule, cholesterol sulfate is able to travel much more freely through the body). Therefore, besides not being able to digest fats as effectively, a person with sulfur deficiency may not be able to fight off pathogens in the intestines as readily, increasing not only the chances of infection but also potentially leading to an overactive immune response (which may be diagnosed as an autoimmune condition like Crohn’s disease, for instance).
Sulfur deficiency may lead to detoxification-related issues in some cases, as well. As a detoxifying agent, sulfur can help clear out pathogens and toxins from the liver, kidneys, and other organs. Without adequate amounts of sulfur, a person may find it more difficult to go through the detoxification process effectively.
Sulfur may also help encourage bile secretion for the liver and gallbladder.
MSM is a supplemental source of sulfur that is safe to consume to correct sulfur deficiency. If you don’t have access to MSM, amino acid supplements like cysteine and methionine may also be effective treatments. Also aim to eat sulfur-rich foods like cruciferous vegetables, garlic and onions, eggs, dark leafy greens, nuts, meats, and seafood (though keep in mind that if you live in an area where the soil may be deficient in sulfur that the vegetables you eat may not be as rich in sulfur as they should be; if you’re trying to correct a deficiency, supplements are the best way to go in most situations).
How to Take MSM
MSM should be taken in medicinal doses over time for the best results. This medicine accumulates in the body over time and generally starts to have medicinal effects after at least 1 month of use. A lot of people don’t notice any major changes until after this amount of time. With a medicine like MSM, it’s important to stick with it for AT LEAST 1 month, if not longer than this, to see what the actual effects will be.MSM can be taken at a dose of 3g (3000mg) per day. It is most bioavailable when taken in its powder form (often, these powders come with a serving cup and you can follow the instructions on the bag or container, if you wish), and should be dissolved in a glass of water. Be aware that MSM is rather bitter. Some people may prefer to mix their daily dose of MSM in with a larger quantity of water, while other people may want to mix it with less water to “get it over with” (the choice is yours, either way of taking MSM is fine as long as you do mix it with water).
A dosage of up to 6 grams daily taken in divided doses over the course of 12 weeks has been used to treat osteoarthritis, though a dose of 4.8 grams has been established to be safe by some studies. Increase your dosage slowly, starting at 1 gram per day. Don’t exceed the 4.8 gram dose until after at least 1 month, and only increase the dose if it seems necessary (if you’re experiencing positive results, keep taking the dose that you’ve been taking; only increase the dose slowly if you’re not seeing any difference, good OR bad).
The side effects of MSM are limited, and this medicine is generally considered to be very safe. In some people, high doses may cause bloating, diarrhea, headaches, insomnia, nausea/vomiting, itching, or the worsening of allergy symptoms. Do not combine MSM with alcohol since this is a medicine that contains sulfur.

Related Posts:
Resources:

 MSM(Methylsulfonylmethane) Powder,1 KG | 2000mg Perserving, MSM Crystal Powder Fortified with Vitamin C, Bioactive Source of Sulfur, Joint Health Support & Hair Growth, Vegan, Non-GMO
MSM(Methylsulfonylmethane) Powder,1 KG | 2000mg Perserving, MSM Crystal Powder Fortified with Vitamin C, Bioactive Source of Sulfur, Joint Health Support & Hair Growth, Vegan, Non-GMO
 Allergy Research Group - L-Methionine 500 mg - Liver and Energy Support, Methylation - 100 Vegetarian Capsules
Allergy Research Group - L-Methionine 500 mg - Liver and Energy Support, Methylation - 100 Vegetarian Capsules
 BULKSUPPLEMENTS.COM MSM Powder - Methylsulfonylmethane, MSM Supplement, MSM Crystals - MSM Pure Powder, MSM 3000mg - Joints Supplements, Gluten Free, 3000mg per Serving, 1kg (2.2 lbs)
BULKSUPPLEMENTS.COM MSM Powder - Methylsulfonylmethane, MSM Supplement, MSM Crystals - MSM Pure Powder, MSM 3000mg - Joints Supplements, Gluten Free, 3000mg per Serving, 1kg (2.2 lbs)