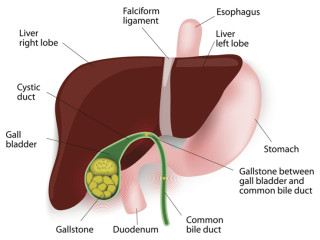
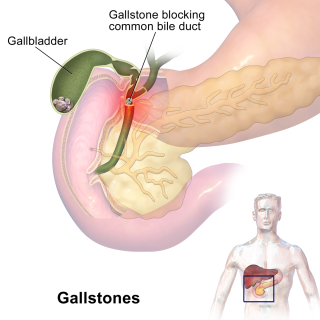
The Connection Between Gallstones, Gallbladder Problems, and Morning Sickness
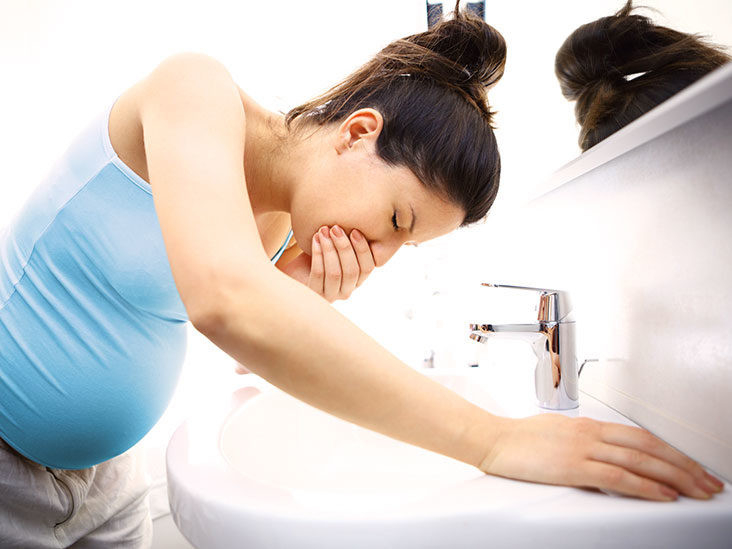
The gallbladder plays a pivotal role in the development and severity of morning sickness during pregnancy. Many of the factors that worsen an existing case of morning sickness are directly correlated to a suffering gallbladder. One good example of this is how spicy, greasy foods often aggravate morning sickness. Even traditional remedies such as apple cider vinegar in warm water point to morning sickness being a gallbladder-related problem. In this article, I’ll connect the dots between gallbladder problems and morning sickness.Why are gallstones more likely to develop during pregnancy?
Women are already statistically more likely to develop gallstones than men, and pregnant women are even more likely still to develop this problem than women who aren’t pregnant or haven’t been pregnant recently. One of the factors that some people attribute this to is the presence of progesterone in particular, a hormone that is produced in the highest quantities in women who are pregnant (in comparison with men or women who aren’t pregnant). The hormonal changes of pregnancy are closely linked to the development of not only gallstones, but also to the development of other liver and gallbladder issues, including cholestasis (slow movement of bile through the bile ducts) and fatty liver of pregnancy. This book specifically talks about the gallbladder, but it’s worth noting that some liver problems can also arise as a result of high progesterone levels under the right circumstances.Higher levels of progesterone during pregnancy ultimately mean that the flow of bile into and from the gallbladder slows down. Progesterone relaxes muscles throughout the body, which is important in order for the woman’s body to be able to adapt to the growing baby and for her body to be able to handle birth appropriately, but it can also cause issues when it comes to digestion (since it can also cause the muscles of the gallbladder and intestines, for instance, to relax a little too much; constipation is an excellent and common example of a symptom caused by this during pregnancy).
Increased estrogen levels also contribute to gallbladder problems during pregnancy. This hormone can increase cholesterol secretion, which can lead to a higher risk of gallstone development, especially given the other factors in play when a woman is pregnant. Since gallstones are often made of cholesterol, when excess cholesterol builds up in the gallbladder, it’s more likely that stones will form, especially when the flow of bile to and from the gallbladder is already sluggish (in this case, likely due to increased progesterone levels).
When bile flow is slower than normal, this can contribute to the development of bile buildup in the gallbladder. This buildup may simply be bile sludge, or it may develop into actual hardened deposits or even fully blown gallstones depending on the situation. Any one of these, though, can lead to blockages in the bile ducts and the eventual formation of gallstones, if they haven’t formed already. Without sufficient bile flow, and with the development of sludge, bile deposits, or gallstones, meals consisting of lots of spicy or greasy foods (or even the smell of these foods, perhaps) can cause nausea, vomiting, and indigestion.
Estrogen and the Gallbladder
Having balanced, well functioning hormones can make a huge difference when it comes to health, happiness (literally), and overall well-being. Interestingly, while hormones during pregnancy have an effect on the gallbladder, the gallbladder’s ability to function well (or not) also plays a role in general hormone health. This is especially true when it comes to maintaining appropriate estrogen levels.Bile is essential for the breakdown of estrogen. Without sufficient bile, or when bile flow is impaired or slow, estrogen breakdown is also affected. Therefore, gallbladder issues, such as gallstones, can lead to higher-than-normal estrogen levels as well as the resulting symptoms of excess estrogen, including acne, tender breasts, water retention, muscle cramps, and more. Other notable symptoms of excess estrogen during pregnancy include these (note that all of these symptoms are also related to gallbladder dysfunction):
- Nausea
- Swelling in the ankles, feet, and fingers
- Spider veins
Other Changes to the Biliary System During Pregnancy
Interestingly, there are some different aspects of biliary function that reliably change in women who are pregnant. These changes are such that they can contribute to the development of gallbladder problems, like gallstones, during pregnancy, but since biliary function goes back to its normal state after birth, any gallbladder problems that developed during a pregnancy are likely to reverse themselves postpartum. Some of these unusual changes that occur in the biliary system during pregnancy include these:- There are fewer enterohepatic cycles. This means that the overall number of times in a day that the woman’s body circulates bile salts from the liver, into the intestines, into the blood, and then finally back to the liver again is decreased. This can contribute to buildup in the gallbladder and the development of gallstones and/or sludge or deposits.
- The total amount of bile acids in circulation increases by about 50% in pregnant women. Again, this is a contributing factor in the development of gallstones.
- Incomplete emptying of the gallbladder following a midday or evening meal has also been reported in some pregnant women. Normally, when a person eats a larger meal, the gallbladder empties out bile into the intestine to digest the food. When there isn’t enough bile to digest the food, whether due to gallstones, incomplete emptying of the gallbladder, or inadequate bile production, for example, this can cause symptoms of indigestion. In this specific case, incomplete emptying of the gallbladder means that the bile in the gallbladder is more likely to form sludge or stones since it’s sitting there “stagnating” for longer.
Click here to subscribe to the Living Database!
The Risks of Gallbladder and Liver Problems During Pregnancy
This list is not intended to be scary, but rather to inform readers in regard to what kinds of problems gallbladder and liver issues can cause during pregnancy. Some of these problems are said to be due to “unknown causes”, but in reality may show a close link to some kind of gallbladder or liver problem (such as gallstones). Not all of the risks listed below are caused exclusively by problems in these two organs, but liver/gallbladder problems may at the very least be a contributing factor in these situations listed below:- Problems potentially caused by cholestasis:
- Premature birth
- Stillbirth
- Passage of meconium before birth
- Dark urine, jaundice, and itching all over the body in the mother
- Problems potentially caused by liver cirrhosis:
- Miscarriage
- Premature birth
- Varicose veins (especially those around the esophagus, known as esophageal varices)
- Problems potentially caused by hepatitis infections:
- Premature birth
- Infertility/difficulty becoming pregnant
- Miscarriage
- Risk of transmission of the infection to the fetus
- Jaundice in the mother
- Increased symptom severity (in the case of a hepatitis E infection)
- Problems potentially caused by fatty liver of pregnancy:
- Nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, and jaundice in the mother
- Preeclampsia
- Death (of either the mother and/or fetus in severe cases)
- Problems potentially caused by gallstones:
- Morning sickness / Hyperemesis gravidarum
- Heartburn
- Back pain or abdominal pain
- Gas, bloating, constipation/diarrhea, etc.
- Preterm birth (in more severe, untreated cases)
How often is morning sickness really caused by gallstones or gallbladder problems?
Many women (and men too, for that matter) go years and years without ever considering that they may have gallstones. Low level pain or discomfort, such as occasional nausea after eating certain foods, intolerance of fats or oils, shoulder blade or upper back pain (specifically in the right shoulder), regular gas and bloating, constipation and/or diarrhea, and other similar symptoms are all indicators of gallstones and gallbladder issues. Some people have more notable symptoms than others, and some people don’t even have any symptoms at all. During pregnancy, any gallbladder problems a woman had before conception are likely to worsen due to the increase in progesterone and estrogen.Studies have acknowledged that pregnancy is a kind of “risk factor” for the development of gallstones, especially in women who have a history of gallbladder issues. The actual number of women who have or develop gallstones during pregnancy is difficult to tell since many women won’t get screened for gallbladder-related problems, and those that do have gallstones (with or without morning sickness) are unlikely to ever find out. Thus, I assume the number is higher than what most studies indicate, but I’ve still included some important research points below:
- One study done in 2006 suggested that between 5-12% of pregnant women have gallstones. The same study estimated that between 3.5-10% of all pregnant women have asymptomatic gallstones.
- A California study observed that 15% of pregnant participants had biliary “sludge” at the beginning of their pregnancies, and that new sludge developed in 30% of the women by the end of their pregnancies.


"The Natural Women's Health Guide... to Pregnancy - BUY HERE!"
Are you trying to resolve an important health problem? Subscribe to the AlivenHealthy Living Database NOW!
The AlivenHealthy Living Database is the tool that Lydian and I use to organize the data that we find while researching cures for diseases each day. Big Pharma, Big Food, and Big Ag work hard to hide the cures for diseases as well as the underlying causes of major diseases to maintain their profits. So it's hard for the average person to find scientific data about cures for disease even though the data exists! So, when Lydi and I find a cure for disease in the scientific literature or if we find anecdotal reports of disease cures that have worked for other people, we compile this information in our Living Database. Recently, we made this database available to the public via subscription so that more people could find links to studies and reports of cures for major as well as minor and even rare diseases.
Click here to learn more about how to subscribe to the AlivenHealthy Living Database.
Related Posts:Resources:

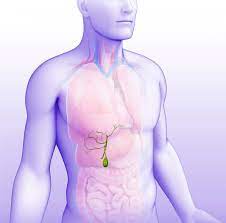 The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped sac just below the liver on the right side of the body, as pictured in this illustration.
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped sac just below the liver on the right side of the body, as pictured in this illustration. The Conditions of Pregnancy Living Database, BETA Release - NOW AVAILABLE! Click here to learn more...
The Conditions of Pregnancy Living Database, BETA Release - NOW AVAILABLE! Click here to learn more...