Melatonin Supplementation During Pregnancy: It's Not Just for Insomnia Treatment.
Have you ever wondered how a woman’s body knows when menstruation is supposed to begin or end? Have you ever wondered how the body knows when a baby is supposed to be born? Perhaps you’ve never considered the idea that women’s bodies are naturally attuned to nature, cycles, and seasons. As humans, we’re fertile year round, but many mammals only reproduce seasonally. Circadian rhythms thus play an important role in the life of all mammalian females. But how do our bodies “know” when it’s day and when it’s night? This is, of course, a question that can’t be answered comprehensively in just a few paragraphs, but we can tell you that melatonin plays a vital role in maintaining circadian rhythms and the body’s “knowing” in terms of night, day, and seasons.In comparison with other nutrient substances during pregnancy, melatonin has received quite a lot of attention from scientists. It deserves mention here that melatonin is derived from one of the Shikimate Pathway nutrients, L-Tryptophan, which is no longer produced by GMO plants. As such, the lack of L-Tryptophan along with the other Shikimate Pathway nutrients (which include among them, methylfolate, also known as vitamin B9, the nutrient that prevents neural tube defects in fetuses), could explain at least in part, why certain health problems develop during pregnancy. For example, preeclampsia and Intrauterine Growth Restriction are both influenced heavily by melatonin, a nutrient that can only be made in the body if L-Tryptophan is present in sufficient quantities.
Click here to download our book, Root Cause: Common Environmental Toxins and How to Protect Yourself from Them to read more about genetically modified plants, the dangers of organophosphate and bromide-containing insecticides, and how GMO plants differ in nutritionally relevant ways from regular, non-GMO plants.
 The Conditions of Pregnancy Living Database - NOW AVAILABLE! Click here to learn more...
The Conditions of Pregnancy Living Database - NOW AVAILABLE! Click here to learn more...
Melatonin and Recurrent Miscarriage
Melatonin is not necessarily the whole story in regard to circadian rhythms in humans, but it does definitely play a role in women’s reproductive cycles, which means that it is also relevant during pregnancy. Indeed, some women use“lunaception” as a way to tune back into their natural circadian rhythms in order to boost fertility levels and balance melatonin production naturally. In a woman’s body, the two circadian “oscillators” are located, after all, in the brain and in the ovaries. The ovaries, like the pineal gland, produce natural melatonin which means that they’re sensitive to light and dark. This means that the ovaries can suffer from “jet lag” as well as the ill effects of exposure to blue light from electronic devices.Melatonin levels are a key factor regulating the timing of menstrual cycles and interestingly, moonlight exposure can be used to to spur ovulation, regulate menstrual cycles, and also prevent recurrent miscarriage naturally. By using lunaception techniques that involve natural moonlight exposure and avoidance of unnatural sources of blue light, some women have been able to prevent miscarriage naturally.
Exposure to the light frequencies and wavelengths of moonlight alters follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) levels as well as luteinizing hormone (LH) levels. In nature, if a woman was sleeping in total darkness, her pineal gland and her ovaries would secrete a certain amount of melatonin. But, if she were sleeping under the night sky, the amount of moonlight her body is exposed to throughout the month would slowly increase up until the full moon. Under the light of the full moon, the ovaries would secrete less melatonin which would spur ovulation. During the new moon, the ovaries would secrete more melatonin which would spur menstruation.
Other sources of light like fire-light, don’t have the same effect on a woman’s monthly cycle as moonlight. Moonlight wavelengths are at 400 nanometers which is roughly equivalent to a 100-watt lightbulb. In other words, both moonlight and exposure to light from a 100-watt lightbulb can spur ovulation. Exposure to the blue light between 400 and 450 nanometers is powerful to the human body. This wavelength of light contains more energy per packet of photon than other wavelengths of light in the red or green area of the spectrum. Computers, smartphones, and other electronic devices emit this wavelength of light which means that they can play a role in as a cause of recurrent miscarriage.
Pregnant women already have a lot of anxiety about their health and the health of their unborn child and many pregnant women who work at home on the computer experience a lot less stress than women who are not staring at a computer screen, but who are working all day outside of the home. As a pregnant woman, you do the best you can to take care of your baby and yourself and it’s likely these days, that computer-time will be a part of your daily routine. But it’s important to be aware of how blue light exposure effects your body as a pregnant woman, particularly after the sun goes down each night. During the daytime, sunlight exposure and exposure to other light wavelengths is normal. But at night, after sunset, exposure to unnatural forms of light can trigger miscarriage in some women who are particularly sensitive or perhaps imbalanced in terms of their circadian rhythms.
Lunaception has been used not only as a natural way to boost fertility by controlling natural melatonin levels in the body, but also as a way to prevent recurrent miscarriage. Indeed, lunaception can be used to get rid of the problem of spotting between periods by balancing follicle stimulating hormone levels. To use lunaception to prevent miscarriage naturally, you’ll need to make a space where you can sleep in total darkness for at least 3-4 days in the middle of the month. Use blackout curtains, get rid of your nightlight, and cover areas of the house where there might be light coming into your bedroom. Don’t expose yourself to the TV, iPads, or your smartphone, or any electronic device on these 3-4 days of the month. An eye cover won’t work because your skin actually senses light exposure too.
After you’ve done 3-4 nights in total darkness, begin to let moonlight into your bedroom if you can, when the moon is full. If you can’t let in pure moonlight, use a 40-watt lightbulb in your bedroom or a 75-watt bulb in a nearby room to mimic the light of the moon. Expose yourself to this light while you sleep for 3 days. Then return to sleeping in total darkness until it would be time for the next full moon.
Exposure to cycles of light and dark play an important role in female reproduction. Melatonin is a substance that the body manufactures naturally in response to our body’s exposure to darkness. When the pineal gland releases melatonin into the bloodstream, the body is alerted to the fact that it’s nighttime. As melatonin is released for longer and longer time periods each night, the body is also alerted to the fact that it’s winter. When melatonin is released for shorter periods each night, the body knows that it’s summer. Absent all other cues, the relative or presence or absence of melatonin in the blood plays a vital role in ensuring that a woman’s body is synced up to the rhythms in nature. This sync-ing up of women with nature occurs not just for the purposes of reproduction but also for immune system function, metabolic activity, and behavior.

"The Natural Women's Health Guide... to Pregnancy - BUY HERE!"
Melatonin Supplements During Pregnancy
Melatonin is a supplement that’s easy to buy over-the-counter and it doesn’t raise any red flags for a lot of women in terms of its effects on their pregnancy. But this substance deserves a bit more attention just because of its role in female reproduction and menstrual cycles. Studies regarding its utility in pregnancy-related contexts have left a lot of questions unanswered.Lydian began her pregnancy taking melatonin supplements but quickly realized within the first two months of gestation that it was making her feel sick so she stopped taking it.
At every phase in a woman’s reproductive cycle, melatonin is there. It plays an essential role in ovulation, fertilization, embryo implantation, and the regulation of pregnancy. Without melatonin as a powerful antioxidant that removes free radicals from the oocyte while modulating a woman’s immune system function, embryo implantation and proliferation would never occur. Melatonin receptors are present in higher-than-average concentrations in ovaries and in the placenta for this reason, to enhance the probability that embryo implantation will be successful.
But in this article, when we talk about melatonin, we’re talking about natural melatonin that your body produces unless we say specifically that we’re talking about a melatonin supplement.
Some studies, for example, indicate that melatonin can prevent preterm birth. Others, indicate that supplementation can be used to hasten contractions when a woman is having her labor induced. During labor, taking a dose of melatonin makes oxytocin receptors more sensitive to oxytocin. Prior to the release of oxytocin to cause uterine contractions at birth, melatonin influences the internal rhythms of the fetus. Disruption of these internal rhythms can lead to preterm birth. But while studies into the use of melatonin supplementation during labor involve taking a pill to enhance the effectiveness of contractions, studies into the role of melatonin in preterm labor often focus on a woman’s natural melatonin levels and activities that might disrupt those levels such as:
- Night shift work
- Continuous exposure to artificial light, especially after sunset
Nonetheless, there are studies showing that melatonin supplements during pregnancy can increase gestation length and birth weight. But it’s important to differentiate between natural melatonin levels and melatonin supplements. There’s a lot of misinformation out there about the safety of melatonin supplements during pregnancy. While I think that most of the time melatonin supplementation is okay for pregnant women, the fact is, most pregnant women seek to take melatonin to treat insomnia. They have no idea that this supplement plays a major role in reproduction and fetal health. Without this vital information, it’s hard for women to make an informed decision. Indeed, there are melatonin supplements that are sold over the counter and there are prescription melatonin agonists that are not chemically the same as melatonin. These melatonin agonists or analogues would actually get in the way of natural melatonin in the body which would make them dangerous for use during pregnancy. Indeed, these melatonin agonists would wreak havoc on a woman’s menstrual cycle.
So, if you’re trying to find information about the safety of melatonin during pregnancy, I would definitely suggest that you pay attention to how supplementation makes you feel. Natural melatonin levels can be enhanced by simply sleeping in a very dark space.
My own experience with melatonin (retrospectively) was that if I was going to have a miscarriage (I had 3 of them), they would happen either when I would have normally been ovulating or when I would have normally been menstruating. The natural rhythm of my body and my menstrual cycles continued throughout the pregnancy. Indeed, Lydian was born on the night she was due, which kept with the rather reliable rhythm of my menstrual cycles when I wasn’t pregnant. That was over 20 years ago before I spent a lot of time on the computer or staring at an electronic device all day. When Lydian was born, my husband and I lived in a rural area under a wide open sky.
I’m not sure if melatonin supplementation would’ve helped me carry my other babies to term or not as I believe that I had other nutrient deficiencies, namely iodine and vitamin B12 deficiency, that made it impossible for me to get past the initial four months of pregnancy. But for women who are reading this who are trying to figure out –why am I having repeated miscarriages?-- I would definitely suggest 50 mg per day of Lugol’s iodine 2% (20 drops), vitamin K2 / MK-7 at 200 mcg, 200 mcg of selenium, 600 mg of magnesium, a 15/2 mg supplement with zinc and copper, along with a vitamin B100 complex. Darken your sleeping space according to the lunaception guidelines. Take the supplements listed above, and then, if you’re still having insomnia, consider taking a melatonin supplement at 5 mg per night, but pay attention to how it makes you feel. Because melatonin during pregnancy pertains to more than just our ability to sleep well. As pregnant women, melatonin alters our reproductive hormone levels and it also impacts the fetus. Indeed, melatonin is even produced by the placenta, perhaps as a way to tell the fetus when it’s night and when it’s day. So, if you take a melatonin supplement, you need to be mindful of these detail which should be common knowledge. Then, you can make an informed decision for yourself about whether or not melatonin supplements are safe during pregnancy for you.
How many mg of melatonin is safe during pregnancy?
If you decide to do melatonin supplementation during pregnancy, choose a melatonin product that's free of sugars including alcohol sugars and other potentially toxic ingredients. Take 3 mg just before you turn off the lights to go to sleep. You can take up to 6 additional milligrams if you wake in the middle of the night. In other words, take 3-9 mg of melatonin per night for insomnia or as a nutrient supplement to prevent preeclampsia naturally.Below, we talk about higher doses of melatonin (30 mg per night) for treating preeclampsia at home. These therapeutic doses can be administered to naturally treat Fetal Growth Restriction or as an at-home treatment for gestational diabetes. Again, check the product that you intend to buy and steer clear of any toxic ingredients including sugars like dextrose or xylitol that might be harmful during pregnancy.
Melatonin and the Placenta
The placenta contains circadian rhythm genes, also known as “clock genes” that modulate melatonin production. During pregnancy, women become more sensitive to circadian rhythms in part due to the increased synthesis of melatonin produced by the placenta. Serum melatonin levels increase significantly after 24 weeks gestation and again at 32 weeks.Melatonin levels impact the immune system during pregnancy. Control of the “clock genes” are important during pregnancy to regulate T-cell response. Melatonin at proper levels tend to suppress inflammation and prevent inflammatory conditions associated with pregnancy such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and preterm labor. Throughout pregnancy, melatonin crosses from maternal circulation through the placenta and back and is able to penetrate the blood-brain barrier of the fetus. Melatonin levels in pregnant women are much higher than in non-pregnant women due to melatonin production in the placenta, but after birth, melatonin levels return to normal within 2 days. In the placenta, melatonin acts as a protective agent against free radicals among other things.
Studies have shown that melatonin can be used safely during pregnancy for the treatment of insomnia.
Melatonin: Gestational Diabetes Supplement
Gestational diabetes mellitus is one of the most common complications that arise during pregnancy. Strictly speaking, gestational diabetes involves any degree of glucose intolerance that starts during gestation. Gestational diabetes creates a number of risks for the mother and child including preterm delivery, preeclampsia, hydramnios, macrosomia, neonatal hypoglycemia, shoulder dystocia birth injury, Cesarean delivery, neonatal respiratory problems, hyperbilirubinemia, or hypocalcemia.Women who develop gestational diabetes have a 30-70% chance of developing the same problem during subsequent pregnancies and they have a 7-fold increase in the risk of developing diabetes type 2 within 5 to 10 years. Mothers are also at an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease and metabolic syndrome. Based on our research into gestational diabetes, it seems that in most cases, gestational diabetes is caused by liver or gallbladder congestion that is common during pregnancy. The liver, gallbladder, and pancreas are all connected via the common bile duct such that, if bile sludge or gallstones reduce passage through the duct, pancreatic enzymes can get backed up into the pancreas. When this happens, the beta cells in the pancreas can be destroyed by the enzymes. This leads to gestational diabetes. Many women can overcome this problem by doing the Hulda Clark cleanse during pregnancy and by taking a powerful herb for gestational diabetes such as Melissa officinalis / Lemon Balm that not only has a lightly sedative effect on the body, but that also has the ability to regrow beta cells. The use of diabetes foods like baobab fruit powder to naturally lower blood sugar levels can also be helpful along with an anti-diabetes diet.

Melatonin plays an important role in the evolution of gestational diabetes. A decrease in melatonin levels increases glucose transport to embryos. This makes sense in that the embryo would need more energy (in the form of glucose) during the day and it would need less energy at night. An increase in glucose transport enhances the oxidative stress imposed on the embryo by diminishing free radical scavenging activities. This can lead to a variety of problems with the embryo. It doesn’t appear to be the crux of the problem in terms of gestational diabetes, but disrupted melatonin levels still contribute to the overall problem.
Melatonin receptor 1B changes have also been shown to influence insulin secretion and pancreatic glucose sensitivity. These changes play an influential role in the development of gestational diabetes mellitus. If a woman has a genetic predisposition to pancreatic islet beta-cell impairment, insulin resistance that develops during pregnancy can unmask it. In short, studies indicate that melatonin receptors play a role in the regulation of glucose levels during pregnancy. Decreased levels of melatonin have been correlated with an increased risk of glycemic imbalances and melatonin supplementation during pregnancy has been shown to decrease the risk of glycemic disturbances. As such, women who develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy might want to consider melatonin supplementation as part of gestational diabetes protocol that includes both Melissa officinalis and baobab fruit powder.
Melatonin: Preeclampsia Treatment Supplements
Preeclampsia impacts 3-10% of pregnancies. This disorder is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. Diagnosis is based on the presence of high blood pressure that occurs after 20 weeks gestation along with organ dysfunction including kidney injury, liver dysfunction, hemolysis, or thrombocytopenia. Eclampsia can lead to seizures, stroke, and death. The placenta is at the center of preeclampsia as doctors have noted that removal of the placenta leads to a regression of symptoms.Normal blood pressure levels vary in daily, circadian cycles. With this in mind, scientists have done studies to look at how melatonin might influence the “clock genes” that tell our bodies when it’s day-time and when it’s night. These circadian-rhythm-focused studies have shown that melatonin inhibits Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) expression and Hypoxia-Induced Factor-1-alpha, a mediator for VEGF lending credibility to the idea that, in women with preeclampsia, the circadian relationship between the woman and the environment has been lost. Studies have shown that melatonin supplementation at after the sun sets with the avoidance of blue light from computer screens, smartphones, and other mobile devices, often allows doctors to lower the dose of antihypertensive drugs for pregnant women. The use of lunaception techniques and exposure to darkness would be beneficial as yet another natural treatment option for preeclampsia.
In a preeclamptic placenta, impaired functioning leads to inflammation and oxidative stress in the body. Melatonin synthesis is reduced. Preeclamptic placentas have fewer melatonin receptors as well. Some experts believe that melatonin works to relieve inflammation and protect placental cells by reducing genetic errors. Melatonin has been shown to promote proper placental perfusion while preventing damage to blood vessels. At pharmacologically relevant levels, melatonin can reduce hypertension in preeclamptic placentas and as such, it has been suggested that doctors combine melatonin supplementation with other preeclampsia treatments.
Melatonin Supplement for Preeclampsia: Dosage Note that researchers have administered up to 10 mg of oral melatonin three times per night (30 mg total) as an innovative treatment for preeclampsia. These researchers noted modest improvements in the duration of pregnancy of a small group of women with preeclampsia.
Melatonin: Intrauterine Growth Restriction Treatment
Disruption to melatonin levels seems to play a role in Intrauterine Growth Restriction. In animal models of Intrauterine Growth Restriction, altering maternal melatonin levels through continuous light exposure during the second half of pregnancy induced Intrauterine Growth Restriction, for example. Also, in the fetal adrenal glands, disruption of melatonin levels altered the “clock genes” as well as “clock-controlled genes” while changing the rhythm of corticosterone (a “daytime” hormone). The fetal adrenal response to adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is altered by a lack of melatonin. Corticosterone production and genes that produce steroid hormones are also altered. But all of these changes are reversed when the mother receives daily doses of melatonin during periods of darkness at night.Melatonin is vital for proper development and functioning of the placenta which explains why melatonin plays a role in Fetal Growth Restriction. Intrauterine Growth Restriction, also known as Fetal Growth Restriction is a common complication of preeclampsia. In this condition, a fetus does not reach its normal biological growth potential due to impairment in placental function. Placental insufficiency often manifests as Intrauterine Growth Restriction / Fetal Growth Restriction involving the birth of babies that are small for their gestational age.
Blood concentrations of Placental Growth Factor significantly decrease in women with placental insufficiency. Placental Growth Factor promotes the growth and proliferation of blood vessels in the placenta. It also stimulates the proliferation of the trophoblast. Placental Growth Factor measures can be used as a diagnostic marker of preeclampsia. In instances involving Intrauterine Growth Restriction, melatonin concentration significantly decreases to increase levels of cytokines. In studies observing melatonin levels in complicated preeclamptic pregnancies versus uncomplicated pregnancies, samples of umbilical cord blood taken after birth showed the women with preeclampsia had significantly lower levels of melatonin. As such, scientists believe that melatonin levels in the placenta can be used as a biomarker of placental function.
Melatonin to Improve Childbirth Experience and Labor
Uterine contractions are essential for active labor and a vaginal birth. Over the past decade, labor induction has become a common practice to call an early end to high risk pregnancies. Labor is typically induced with the intention of spurring a vaginal delivery, but most induced labors fail in this department and end in C-section. Unfortunately, C-section increases the risk of postpartum hemorrhage and venous thrombosis.Melatonin levels increase over the course of pregnancy, peak during labor, and then fall rapidly after the baby is born. Some experts believe that the melatonin receptor works together with oxytocin to promote nocturnal uterine contractions. Indeed, in humans, spontaneous labor at term starts more often at night. More babies are born at night too when the pineal gland is actively secreting melatonin into circulation. It makes sense that melatonin would increase uterine muscle sensitivity to oxytocin.
In summary, one could say that melatonin plays a biological role in the timing and onset of spontaneous labor. It also plays a role in making uterine contractions effective in vaginal birthing.
In studies that observed light-induced modulation of melatonin secretion on women late in their third trimester (36-39 weeks), studies have shown a positive relationship between melatonin levels and uterine contractions after the 35th week of gestation.
 Click here to subscribe to the Living Database!
Click here to subscribe to the Living Database!
Resources:
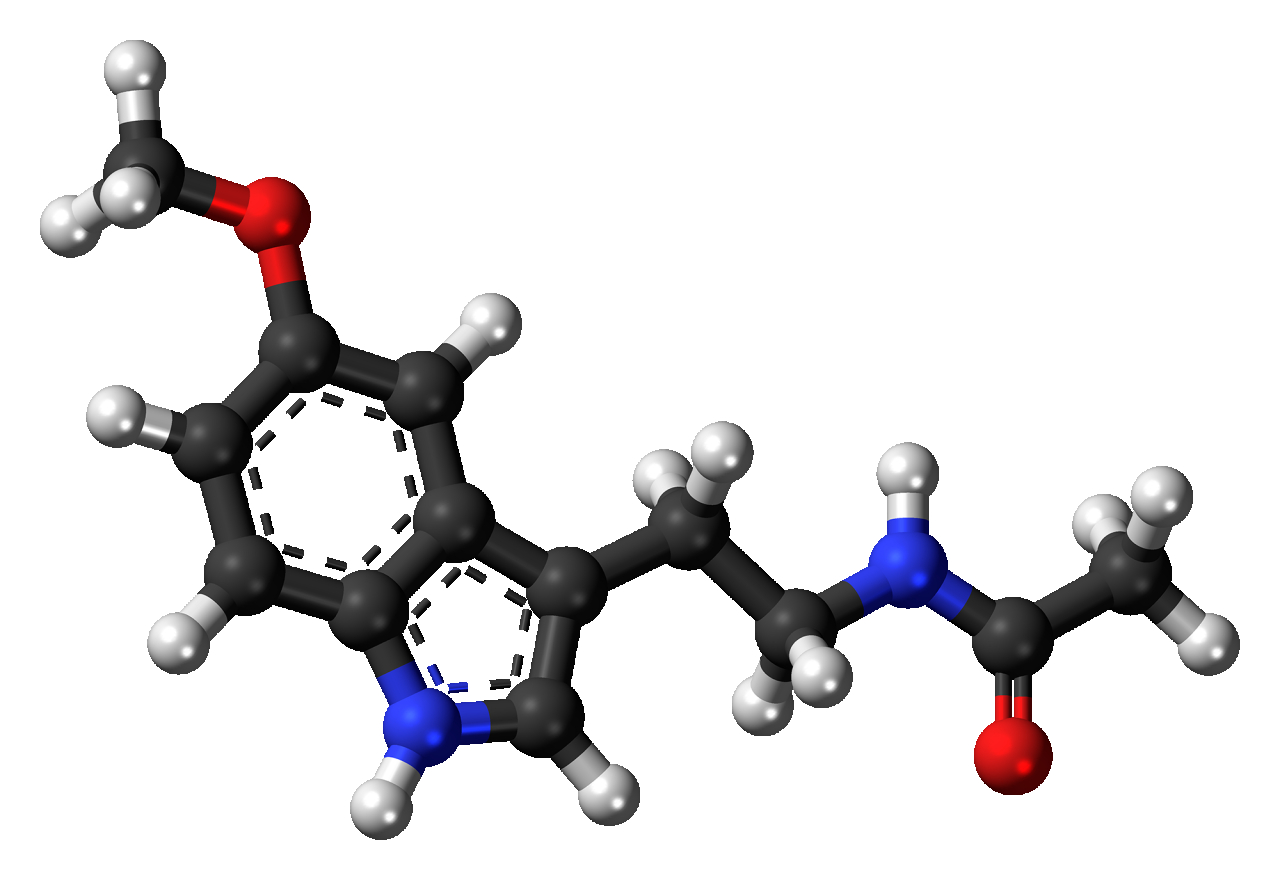
 Though mainstream media and Big Pharma wants women to believe that melatonin is a nutrient-hormone that only impacts sleep, in fact, melatonin is produced not just in the pineal gland, but also in the ovaries, and in the placenta. Melatonin supplements have been heavily studied to show that they're not only safe during pregnancy, but they also help prevent preterm birth, Intrauterine Growth Restriction, gestational diabetes, and preeclampsia.
Though mainstream media and Big Pharma wants women to believe that melatonin is a nutrient-hormone that only impacts sleep, in fact, melatonin is produced not just in the pineal gland, but also in the ovaries, and in the placenta. Melatonin supplements have been heavily studied to show that they're not only safe during pregnancy, but they also help prevent preterm birth, Intrauterine Growth Restriction, gestational diabetes, and preeclampsia. Vital Nutrients Melatonin 3mg | Vegan Sleep Support Supplement to Support The Body's Natural Sleep Cycle* | Gluten, Dairy and Soy Free | 60 Capsules
Vital Nutrients Melatonin 3mg | Vegan Sleep Support Supplement to Support The Body's Natural Sleep Cycle* | Gluten, Dairy and Soy Free | 60 Capsules
 Nature's Bounty Melatonin, 100% Drug Free Sleep Aid, Dietary Supplement, Promotes Relaxation and Sleep Health, 10mg, 60 Count(Pack of 2)
Nature's Bounty Melatonin, 100% Drug Free Sleep Aid, Dietary Supplement, Promotes Relaxation and Sleep Health, 10mg, 60 Count(Pack of 2)