Asparagus officinalis: Herbal Remedy for Alcoholism
Asparagus officinalis is a well-known vegetable that’s available throughout the world, but this vegetable has also been used as an herbal remedy for alcoholism. Asparagus is a supplement that can be used to treat a hangover. It works in large part to prevent hangover because it contains high levels of specific amino acids and minerals that also reduce cravings for alcohol and that generally improve the metabolic function of people who are prone to alcoholism.
The leaves and shoots contain the highest levels of amino acids and minerals so a supplement or medicinal meal that contains these specific parts of the asparagus plant would be most beneficial as a natural, at-home remedy for alcoholism. An Asparagus officinalis leaf extract not only provides nutrients that are helpful as an herbal recovery for alcoholics via the nutrients it contains, but asparagus also is able to decrease free radical production in the liver. This means that asparagus can be taken to treat or to prevent liver damage in alcoholics.
Asparagus officinalis leaf extract is able to upregulate enzymes to twice their normal levels in the body. These enzymes work to metabolize alcohol more quickly and more efficiently. They include:
- Alcohol dehydrogenase
- Aldehyde dehydrogenase
 Click here to buy Asparagus Supplement.
Click here to buy Asparagus Supplement.
Asparagus officinalis supplement dosing:
Asparagus officinalis should be taken at 1600 mg per day to prevent alcohol cravings naturally.

Click here to schedule a health coaching call with us.
Asparagus officinalis, Hypericum perforatum, and Pueraria lobata Combo Herbal Remedy for Alcoholism
While an asparagus leaf supplement works nicely as an herbal remedy for alcoholism and as a nutrient supplement to prevent liver damage due to alcohol consumption, Hypericum perforatum (also known as St. John’s Wort) and Pueraria lobata (also known as Kudzu) work through a slightly different mechanism of action to cure alcoholism naturally.
 Click here to buy St John's Wort Capsules.
Click here to buy St John's Wort Capsules.
St. John's Wort for Alcohol Cravings
St. John’s Wort is perhaps most famous in the western world as a natural antidepressant medicine, but in fact, in the east, this herb is used more often to treat infections, particularly those involving pathogens that live in nervous system tissue. Indeed, in the west, St. John’s Wort seems to work irregularly as an herbal antidepressant perhaps because it is treating pathogens that are infecting nerve tissue to cause mood disorders. In individuals who are not suffering from an infection of nervous system tissues, St. John’s Wort may not work as an antidepressant. There are some associations and correlations between, for example, Herpes and alcoholism and interestingly, both asparagus supplements an St. John’s Wort are herbal cures for HSV infection. Click here to read more about how to cure an HSV infection if you suspect that HSV and alcohol binging is something that's related for you.St. John's Wort Dosing for Alcoholism:
Take 2400 mg twice each day (4800 mg total).
Click here here to subscribe to the Living Database!
Kudzu for Alcohol Cravings
Pueraria lobata or Kudzu, is able to suppress an alcoholic’s need for alcohol by regulating the alcoholic’s blood sugar levels. Alcoholics who take Kudzu at the proper dose prior to a binge tend to consume at least 20% less even if they don’t intend to decrease their alcohol intake. As such, Kudzu as an herbal remedy for alcoholism, diminishes cravings and empowers the alcoholic to begin to take control over how much they drink in a given time. Meanwhile, St. John’s Wort and Asparagus officinalis further support the alcoholic’s effort to quit drinking permanently by providing specific nutrients that an alcoholic needs, by altering certain metabolic functions in the body, and by killing infectious agents like HSV that might be responsible for causing alcohol cravings.Kudzu Dosing:
Take 2400 mg 2 hours prior to drinking, or take 1200 mg up to 4 times daily to prevent or reduce alcohol cravings.
 Click here to buy Kudzu Root Extract Powder.
Click here to buy Kudzu Root Extract Powder.
Resources:
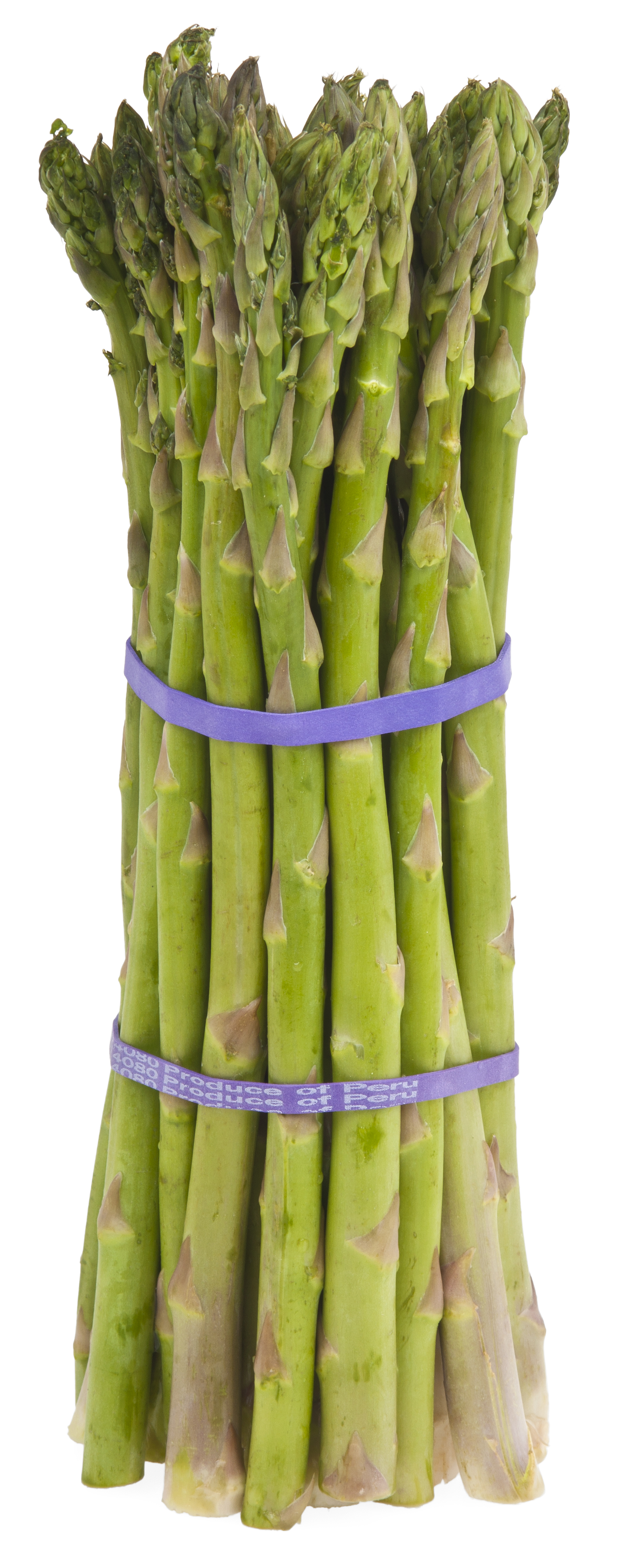
 Asparagus can be used both at mealtime and as a supplement to reduce alcohol cravings naturally.
Asparagus can be used both at mealtime and as a supplement to reduce alcohol cravings naturally. Alcohol Addiction Demystified: The Science of Alcohol Addiction and How to Overcome It At Home - BUY HERE!
Alcohol Addiction Demystified: The Science of Alcohol Addiction and How to Overcome It At Home - BUY HERE!