What is black mold?
What is black mold?
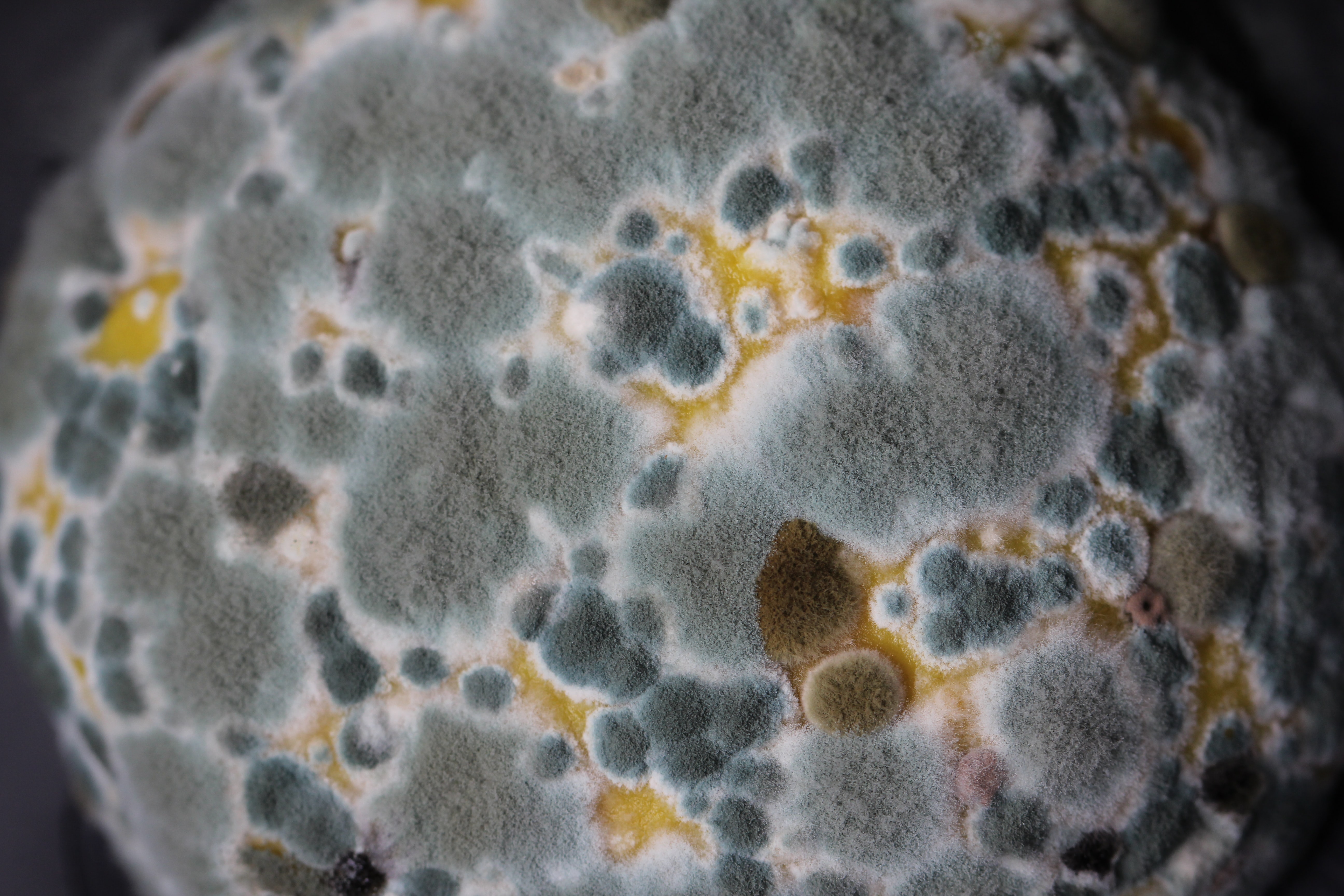
Black mold is often used as a general umbrella term that refers to a group of fungi that are black in color and found in indoor spaces. However, though “black mold” can refer to a few different species of fungus, the most toxic black mold species is Stachybotrys chartarum (which may also be referred to as S. atra or S. alternans). Other species that may be referred to as black mold include:
- Alternaria spp.
- Aspergillus spp. (specifically Aspergillus niger)
- Cladosporium spp.
Symptoms of Black Mold Poisoning/Black Mold Exposure
All of the species of black mold listed above can cause symptoms of black mold exposure/black mold poisoning, and are considered to be deadly molds (in other words, long-term or acute exposure can lead to serious illness or even death). Some of the most common symptoms of short-term or moderate exposure include:- Headache
- Sneezing
- Nasal congestion
- Coughing
- Skin rash
- Septicemia (blood poisoning)
- Red/itchy eyes
- Sore throat
- Sinus infection
People with asthma may experience worsened symptoms when exposed to black mold, as can individuals with chronic respiratory diseases like COPD or cystic fibrosis. Individuals with a true mold allergy may have particularly severe symptoms, while other people experience little to no symptoms at all, especially if exposure to the mold is limited.
Health Problems Caused by Long-Term Black Mold Exposure
Besides the common symptoms of black mold exposure, some types of black mold can cause more serious health problems when a person is exposed to the mold over the long-term. Different molds may cause different health problems (with some crossover, of course) so I’ve organized the potential long-term problems associated with black mold exposure according to the type of mold that may cause them.Stachybotrys chartarum Mold
Stachybotrys chartarum is more commonly referred to as toxic black mold. It thrives in environments with a humidity level above 55% where the temperature is subject to fluctuations. It grows on surfaces with a high cellulose content and low nitrogen content, such as wood, drywall, cardboard, and other surfaces.In contrast with some other forms of black mold, where the mycotoxins are the primary toxic compound and the spores generally are responsible only for a comparatively minor allergic response in most cases, the spores of Stachybotrys mold are also toxic. This means that being in an environment where Stachybotrys is present, even if only for a short period of time, can cause symptoms more readily. Also note that even though the spores of toxic black mold die quickly, they are still allergenic and have toxic effects on the body even after they’re dead.
Some of the long-term health consequences of Stachybotrys mold exposure include:
- Cold and flu symptoms
- Fatigue
- Dermatitis / skin rash
- Diarrhea
- Intermittent local hair loss
- General feeling of being unwell
- Pneumomycosis (fungal infection in the lungs)
- Liver cancer
- Kidney cancer
Case reports have linked unusually high levels of Stachybotrys chartarum exposure to pulmonary hemosiderosis in infants and pulmonary hemorrhage in house cats. Animals that were injected with the Stachybotrys chartarum toxin experienced multi-organ damage, including necrosis, cerebral hemorrhage, and hemorrhaging in the liver, kidneys, heart, lungs, intestines, thymus, spleen, and lymph nodes. Of course, most people won’t be injected directly with the mycotoxin from Stachybotrys chartarum, but it’s worth noting that these organs are likely to be the main ones affected by exposure to this mold.
Aspergillus spp. Mold
Aspergillus spp. is a very common type of deadly black mold that may develop on household surfaces in some cases, but is significantly more common in decaying plant matter and on foods for humans and animals. The mycotoxins and spores of Aspergillus mold can cause the following health problems:- Extrinsic asthma
- Edema
- Bronchospasms
- Pulmonary/lung infection
- Pulmonary emphysema
- Some types of cancer
- Fungal ear infections
- Fungal eye infections
Exposure to Aspergillus mold can also result in the development of aspergillosis, a condition that mostly develops in immunocompromised people who have been exposed to the mold, but may develop in other people as well. Aspergillosis is categorized into three main categories:
- Pulmonary aspergillosis - This form of aspergillosis is most likely to develop in people with lung conditions (like emphysema, sarcoidosis, or tuberculosis) that result in unusual “pockets” of tissue in the lungs. The Aspergillus can grow in these pockets and in some cases may develop a clump of fungus known as aspergilloma or mycetoma. Pulmonary aspergillosis may also be associated with fungal infections in the sinuses and ears. Symptoms may include chest pain, wheezing, fever, coughing (sometimes with mucus or blood), and difficulty breathing.
- Invasive aspergillosis - When an Aspergillus infection leaves the lungs and enters the bloodstream (where it can then travel to the brain, liver, kidneys, or skin), this is known as invasive aspergillosis. It is a more severe form of this condition, and can even result in death if left untreated. Symptoms include cough with blood and/or bleeding in the lungs, fever, chills, shortness of breath and trouble breathing, shock, kidney failure, and liver failure.
- Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) - This type of aspergillosis occurs in people with existing respiratory conditions (like cystic fibrosis, asthma, or bronchiectasis). It is a more severe allergic reaction to Aspergillus mold, and symptoms may include coughing with mucus and/or blood, fever, wheezing, worsening of asthma symptoms, and increased mucus or sputum secretions.
Alternaria spp. Mold
Alternaria spp. mold spores are generally deposited in the upper respiratory tract, nose, and mouth. Symptoms and health problems associated with long-term exposure to Alternaria include:- Pulmonary emphysema
- Bronchospasms
- Edema
- Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis (this may manifest as cystic swellings or abscesses just below the surface of the skin)
- Onychomycosis (a fingernail or toenail fungal infection)
- Dermatomycosis (a fungal skin infection, which may encompass any number of sub-types of infection, such as ringworm, tinea, and more)
- Sinusitis
- Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (a condition that causes the lung tissues to swell and become extra sensitive, leading to problems breathing and lung damage over time)
- Baker’s asthma
- Extrinsic asthma
Cladosporium spp. Mold
Cladosporium spp. molds are found outside more commonly than they’re found indoors, but they can still colonize interior areas as well. In particular, it is found on fiberglass duct liner, as well as on some paints and fabrics or textiles. It may cause the following conditions in humans:- Mycosis (fungal infection; there are many different kinds of mycosis, including of the eyes, ears, skin, and more)
- Extrinsic asthma
- Edema
- Bronchospasms
- Pulmonary emphysema
 Click here to subscribe to the Living Database!
Click here to subscribe to the Living Database!