 NAC as a Natural Cure for COPD
NAC as a Natural Cure for COPD
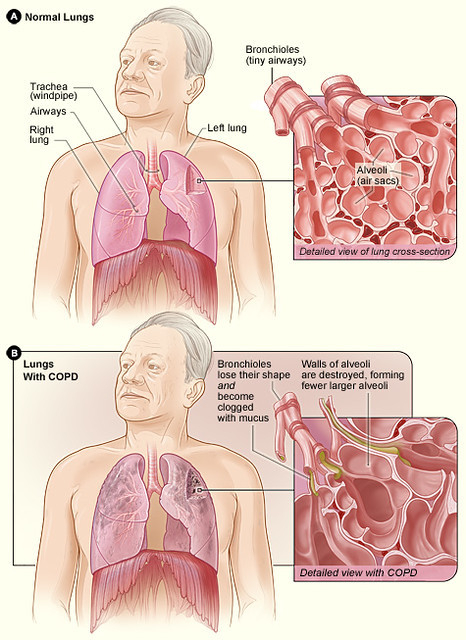
N-Acetylcysteine or NAC is an extremely potent lung tonic and in some cases, it may even be able to cure COPD, though NAC is usually recommended for use with the other treatments we discuss in this series (molecular hydrogen and supplemental oxygen, hypertonic saline and hyaluronic acid nebulization, dry halotherapy and chlorine dioxide). NAC, Acetylcysteine, and Cysteine are all related substances. Individuals who cannot obtain NAC may be able to find Acetylcysteine or Cysteine to use as alternatives to NAC. Patients with COPD can benefit a great deal from taking NAC as a natural supplement detoxifier to increase the flow of mucus and their ability to expel mucus from the lungs. Patients who are not taking corticosteroids are most likely to benefit from the use of NAC. Corticosteroids can reduce the benefits of NAC treatment.

Click here to schedule a health coaching session with us.
NAC, Acetylcysteine, and L-Cysteine are all powerful antioxidants and some scientists believe that in addition to its ability to thin mucus, it also works to heal the lungs by counteracting the effects of oxidants from cigarette smoke or other toxins and pathogens in the body. (For the sake of brevity, we'll refer to NAC, Acetylcysteine, and L-Cysteine as just "NAC" from here forward unless specifically noted). NAC is an anti-inflammatory that reduces swelling in the lungs and airways. Though conventional medicine does not offer any kind of therapy that can stop COPD from getting worse, NAC is a natural medicine that influences lung healing through several different pathways including the following:- NAC provides sulfhydryl groups that act as a precursor of reduced glutathione.
- NAC functions as a reactive oxygen species scavenger to balance the redox status of lung cells and other cells in the body.
- By changing the redox status of cells, NAC can reduce airway inflammation in COPD.
- NAC reduces the viscosity of sputum to clean the bronchioles and lung tissues.
Click here to learn more and subscribe to the Living Database now.
NAC is a precursor to glutathione, a detoxifying substance in the body. Scientists who have tested these substances in COPD have found that patients who take NAC on a regular basis at higher doses (1000 to 6000 mg daily) have a reduction in COPD symptoms, fewer exacerbations of the disease, and a lesser risk of lung function decline. Essentially, NAC reduces the symptoms of COPD and it heals the lungs over time by reducing inflammation in the airways.Acetylcysteine has also been studied by scientists as a cure for COPD and chronic bronchitis. It has the following effects on COPD patients:
- Acetylcysteine reduces the viscosity of sputum.
- It reduces the severity of coughing.
- It reduces the number of bacteria found in the airways.
- It reduces the severity and number of influenza-like episodes.
- It reduces the number of exacerbations of the disease and the number of hospital admissions in COPD patients.

Click here to subscribe to the DreamLight.app, a brain entrainment, guided meditation tool to reduce stress and overcome trauma.
In studies on Acetylcysteine, patients who were using inhaled corticosteroids did not experience the same benefits from taking Acetylcysteine as patients who were not using inhaled corticosteroids. Studies on NAC have yielded similar results in which patients who are using inhaled corticosteroids do not experience the same benefits as those who are not. In other words, if you wish to use NAC, Cysteine, or Acetylcysteine as a natural cure for COPD, it may be in your best interest to switch to molecular hydrogen inhalation as a way to reduce airway inflammation as opposed to using bronchodilators or other medicines that contain steroids or corticosteroids.Take NAC, Acetylcysteine, or L-Cysteine at 1000 mg up to 3 times per day to improve symptoms of COPD. Or use Mucomyst Acetylcysteine for Nebulizing.
 Click here to buy L-Cysteine.
Click here to buy L-Cysteine.
NAC and Chlorine Dioxide: How to Use These Medicines Together
One of the most important medicines that we recommend as a cure for COPD is chlorine dioxide solution. But NAC and chlorine dioxide work through opposite mechanisms of action. This can be a positive thing in that the use of NAC and chlorine dioxide allows the body to rebalance. But it’s important that doses of NAC and chlorine dioxide are properly spaced or else these two medicines can cancel out the beneficial effects of each other.NAC has a half life between 5.6 and 6.25 hours. What this means is that after you take NAC, it takes about 6 hours for half of it to leave your body. In contrast, chlorine dioxide has an extremely short half-life of only about an hour. So if you want to get the best results from taking NAC and chlorine dioxide, timing is important. We recommend that you take NAC at bed-time, about 1 hour after your last dose of chlorine dioxide, giving NAC plenty of time to work without interfering with morning doses of chlorine dioxide.

Click here to buy The Textbook of Scientifically Proven, Holistic Cures for Chronic and Infectious Respiratory Disease.
Resources: