 Hypertonic Saline as a Non-Toxic, Natural COPD Treatment to Reverse Lung Deterioration
Hypertonic Saline as a Non-Toxic, Natural COPD Treatment to Reverse Lung Deterioration
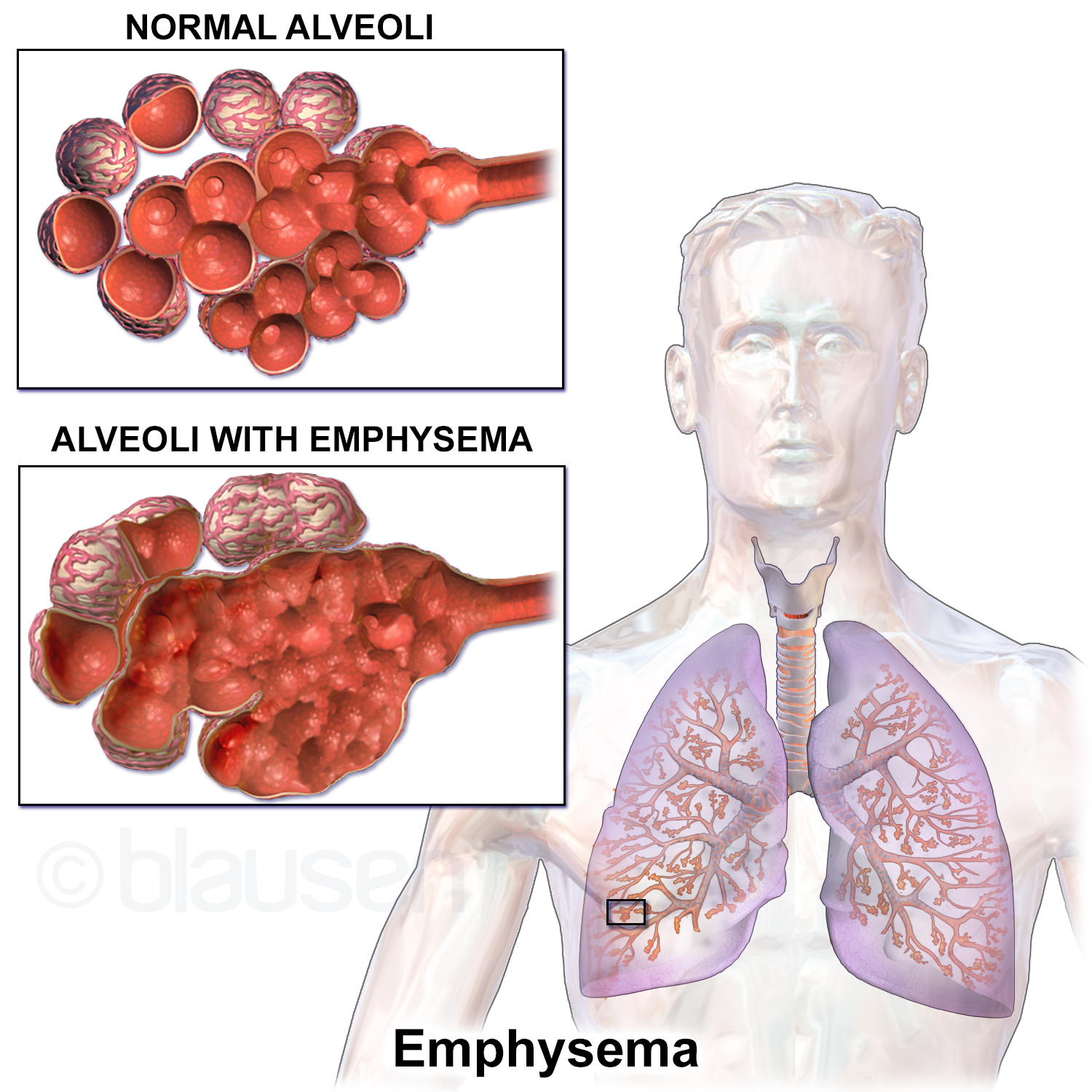
One of the issues that many COPD patients experience is an inability to cough up mucus stuck in the lungs. Mucus is a substance that the body produces to stick to toxins or pathogens that can then be moved out of the body or prevented from entering the body (as in the nose). As such, mucus ideally should not be too viscous. Mucus should be able to “flow”. And mucus needs to be able to move from areas with toxins or pathogens into organs of digestion and then detoxification such as the intestines, liver, or kidneys.
Individuals with COPD may struggle to cough up mucus from the lungs, but scientists have found that hypertonic saline 5-7% can naturally help COPD patients cough up sputum and mucus from the lungs more easily. Salt by itself has long been used as an important treatment for lung disease, after all. Many years ago, scientists realized that people who worked in salt mines tended to be significantly less vulnerable to lung diseases like COPD. Salt functions an anti-infection agent, but it also helps keep the lungs properly hydrated in patients with certain severe types of lung disease. Salt causes water to stay on the surface of lung tissues longer, allowing those lung tissues to slide more easily past each other, while making mucus thinner and easier to cough up out of the lungs. Indeed, scientists have noted that hypertonic saline works on many levels to clear the lungs of toxins and pathogens while generally healing the tissues.
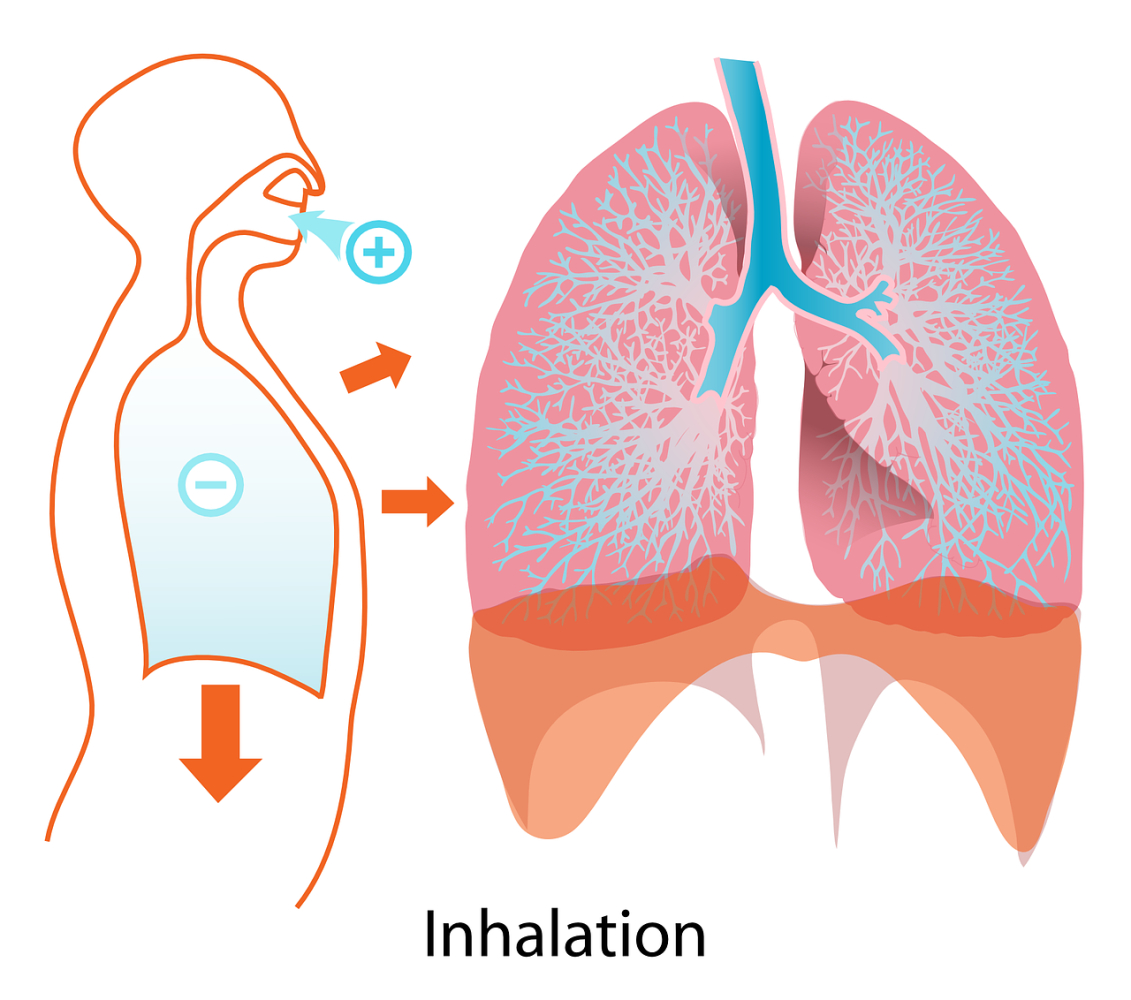
Hypertonic saline is administered to COPD patients using a nebulizer. During the first 1 to 10 treatments, COPD patients need to have a medical professional present because the saline may cause coughing (a desirable effect) as well as airway constriction. Most COPD patients don’t experience airway constriction after the first 10 treatments with hypertonic saline.

Click here to schedule a health coaching session with us.
Nebulizing Hypertonic Saline as a Natural COPD Treatment
The use of nebulized hypertonic saline as a natural cystic fibrosis treatment is very effective with long term use and that can halt the progression of that disease which is what alerted scientists to its possible utility as a natural treatment for COPD. Hypertonic saline works through several different mechanisms of action to thin mucus, spur the cough reflex, and to lubricate airways to make it easier for the lungs to remove mucus. The salt also has an anti-infection effect on lung tissues.Hypertonic saline at a concentration of 6 to 7% has been scientifically shown to be effective as a natural cure for COPD. It is administered via a nebulizer and in some cases, it may be beneficial to add 0.1% hyaluronic acid to the saline to reduce airway constriction and to make the treatment more pleasant in terms of taste.
Hypertonic saline, in addition to its anti-infection function, prevents the formation of biofilm in the lungs, which reduces the risk of developing a severe antibiotic resistant infection from certain bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Additionally, this simple, natural substance increases levels of natural detoxifiers in the lung tissues such as glutathione and thiocyanate which protect the lungs from oxidative lung injury similar to molecular hydrogen.
As a COPD cure, hypertonic saline is administered in concentrations of 6-7% twice daily via nebulizer. Use of the saline solution twice daily for 30 minutes improves lung function and to halt the progression of COPD. This medicine should be administered regularly and consistently for at least 1 year to reverse COPD, prevent emphysema, and spur the healing process.
Click here to learn more and subscribe to the Living Database now.
Nebulizing Hypertonic Saline and Hyaluronic Acid as a COPD Cure
Some COPD patients may not respond well to the use of plain, high-concentration hypertonic saline as a nebulizing agent. A common side effect is coughing, but young patients may not like the salty taste of the treatment either. Adding 0.1% hyaluronic acid to the nebulizer along with 6-7% hypertonic saline can improve the taste and also reduce coughing. Indeed, the use of hypertonic saline along with hyaluronic acid stops the progression of COPD and improves lung function over time.Do not add just any hyaluronic acid product to hypertonic saline as a lung treatment for use in a nebulizer. Most “pure” hyaluronic acid products actually contain toxic chemicals that should never nebulized. Rather, purchase a product that contains the proper proportion of hypertonic saline and hyaluronic acid specifically for nebulizing into the lungs.
Click here to buy Hypertonic Saline 7%.
Using Hypertonic Saline to Cure COPD: What You Need to Know
If you’ve never used hypertonic saline solution in a nebulizer to treat COPD naturally at home, then you need to be aware of the fact that the first treatment with hypertonic saline can cause temporary narrowing of the airways and coughing. Doctors often administer a bronchodilator to prevent narrowing of the airways during the initial treatments with hypertonic saline. Often, narrowing of the airways during nebulizer treatments with hypertonic saline and hyaluronic acid lessens considerably after the first 10 doses.At AlivenHealthy, we generally do not recommend that patients with COPD use pharmaceutical bronchodilators that often contain steroids. Indeed, women, especially, should be aware that the administration of steroids can disrupt their hormones and ultimately cause additional lung problems and breathing issues over time. A possible alternative to the use of a bronchodilator would be the inhalation of molecular hydrogen for 45 minutes just prior to using the hypertonic saline solution mixed with hyaluronic acid 0.1% in a nebulizer. The hypertonic saline and hyaluronic acid mixture will be less likely to cause coughing and airway constriction than hypertonic saline by itself and the use of inhaled molecular hydrogen will decrease inflammation in the airways prior to the administration of the hypertonic saline and hyaluronic acid treatment.
NOTE: Be sure to read our article about nutrition and chronic lung diseases to learn about how many of the drugs that are prescribed for COPD patients reduce potassium levels, which in turn, can lead to a worsening of COPD symptoms.

Click here to buy The Textbook of Scientifically Proven, Holistic Cures for Chronic and Infectious Respiratory Disease.
Resources: