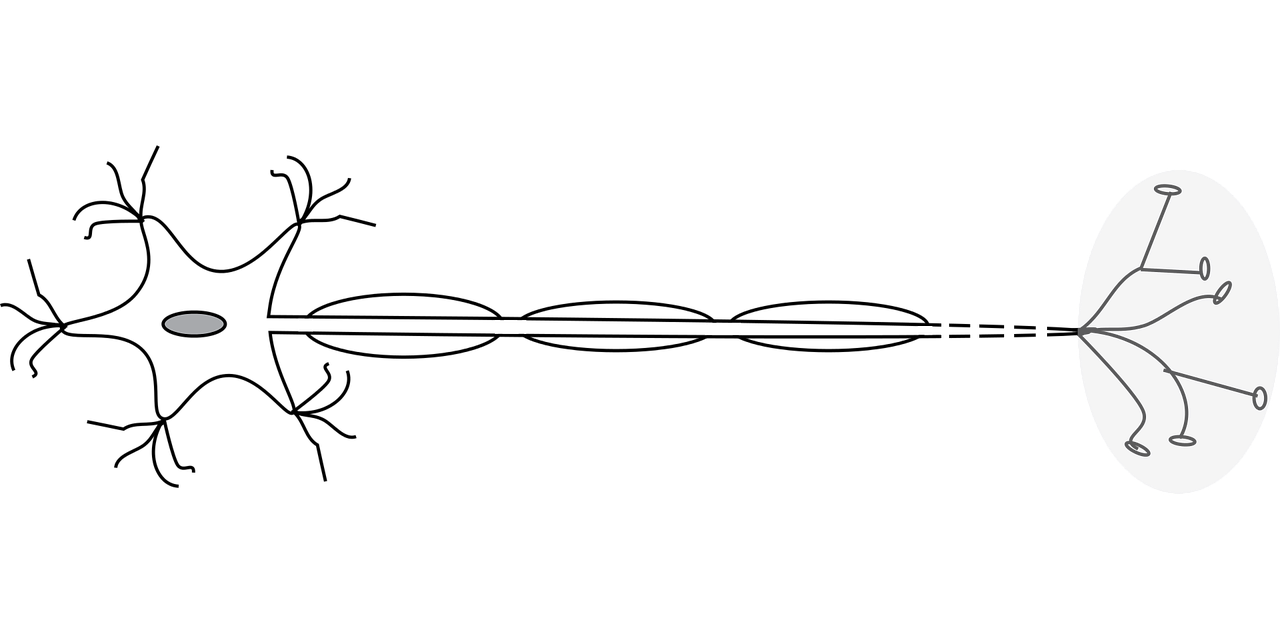 Transverse Myelitis, Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis, and Other Post-Vaccine Demyelination Diseases
Transverse Myelitis, Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis, and Other Post-Vaccine Demyelination Diseases
Transverse myelitis is a disorder that occurs when both sides of an area of the spinal cord become inflamed. The inflammation in transverse myelitis often leads to destruction of the myelin sheaths on the nerve cell, or even nerve cell death. This can cause symptoms such as chronic pain, muscle weakness, sensory problems, urinary retention or incontinence, bowel dysfunction, or even paralysis. Infection or other concurrent immune system disorders are generally considered to be the primary causes of transverse myelitis (COVID-19 is among the viral and bacterial diseases that can cause the onset of transverse myelitis, so it can be reasoned that the COVID-19 vaccine or vaccines for other causal diseases may also play a role in this disease’s development in some cases).
Vitamin B12 deficiency has been strongly connected to neuropathy and myelopathy, with some cases of transverse myelitis being correlated with an accompanying deficiency in this vitamin. One case study observed a man with vitamin B12 deficiency and secondary transverse myelitis (meaning that the transverse myelitis developed after and as a result of the nutritional deficiency). This man had been experiencing symptoms for over a year at the time that he received treatment, so researchers speculate that he would have recovered more fully and more quickly had he started vitamin B12 therapy sooner. Even still, the researchers noted that for people with secondary transverse myelitis, intravenous/injection-based vitamin B12 therapy can help begin to treat the disease within 3-6 months (full recovery may take longer than this, but changes become evident within this time).
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM) generally develops within 7-21 days after a vaccination. The initial symptoms may include headache, vomiting, fever, and drowsiness, which usually progress to include confusion and disorientation, stupor, paralysis, incontinence or urinary retention, coma, and seizures. In some particularly severe cases, ADEM can result in death. Encephalomyelitis occurs primarily in the brain, but due to its similarity with transverse myelitis, the orthomolecular treatment for ADEM may be similar.
Other demyelination disorders or health problems resulting from demyelination that may benefit from a similar orthomolecular treatment as described above include:
- Neuromyelitis optica (Devic’s disease)
- Chronic inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy
- Impaired muscular coordination
- Loss of sensation (sight, touch, smell, etc.)
- Paresthesia
- Ataxia (loss of voluntary movement)
- Clumsiness
- Speech and hearing problems
- Progressive inflammatory neuropathy
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
- Myelopathies
- And more…
 COVID-19 and Respiratory Infection Self treatment and Prevention BUNDLE - Volumes 1, 2, and 3
COVID-19 and Respiratory Infection Self treatment and Prevention BUNDLE - Volumes 1, 2, and 3

The Post-COVID Vaccine Recovery Book and Autoimmunity Reference Guide
 Everything You Never Wanted to Know About the Treatment of Chronic Pain... and How to Avoid Painkillers That Will Eventually Kill You - BUY HERE!!!
Everything You Never Wanted to Know About the Treatment of Chronic Pain... and How to Avoid Painkillers That Will Eventually Kill You - BUY HERE!!!

Related Posts:
Resources: