The Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Diet Protocol
Diet plays an important role in the development and treatment of disease. The same is true for PCOS. Eating nutrient rich foods that include primarily fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, free-range and non-processed meats and animal products is extremely important regardless of which diet you choose. However, for women with PCOS, the ketogenic diet may be particularly valuable as a therapeutic treatment (in other words, you may not have to follow the ketogenic diet forever, but it may help your body heal and reset more successfully than other diets).The ketogenic diet has been used successfully for many years as a treatment for diabetes, metabolic syndromes and diseases, and weight loss. It has also been used to treat acne, heart disease, epilepsy, and various nervous system disorders (such as Parkinson’s disease). Since many of the situations where the ketogenic diet really shines are actually closely related to the root causes of PCOS, it makes sense that this diet has been shown to be reasonably effective in the treatment of polycystic ovarian syndrome as well.
One study examined the efficacy of the ketogenic diet in the treatment of PCOS-caused obesity in 14 women over the course of 12 weeks. After these 12 weeks, the women following the ketogenic diet exhibited a significant decrease in overall body weight, BMI (body mass index), and FBM (fat body mass), as well as a slight decrease in LBM (lean body mass). “Good” (HDL) cholesterol levels increased while triglycerides and overall cholesterol levels, including “bad” (LDL) cholesterol levels, decreased notably. Insulin resistance was decreased as well. The women’s estradiol and progesterone levels increased after treatment.
The specific diet followed in this study was a modified form of the ketogenic diet known as the KEMEPHY diet, which is a combination of the Mediterranean diet and the classic keto diet. The participants consumed between 1600-1700 calories per day. On this diet, the women were allowed to eat the following foods:
- Unlimited leafy green vegetables, zucchini, cucumbers, cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, etc.), and eggplants.
- Limited eggs, meat, and fish (120 grams of meat OR 20 grams OR 2 eggs each day)
- High protein, 19 grams of protein per portion
- Low carbohydrates, 3.5 grams per portion
The study also required the participants to consume 4 different herbal extracts, each of which contained multiple herbs. Some of the notable herbs contained in these extracts were licorice, juniper, ginger, ginseng, flaxseed, dandelion, and anise. The link to this study is in the resources below for interested readers (the study provides a full list of the ingredients in these tinctures).
It should be noted that this particular study did not analyze the effects of the ketogenic diet on oligomenorrhea or infertility. However, the ketogenic diet in combination with other therapies discussed in this section that specifically target these two symptoms of PCOS may offer an effective treatment protocol.
 The Natural Women's Health Guide, Volume 2 - Fertility, Natural Fertility Enhancers, Infertility Treatments, and Natural Libido Boosters - BUY HERE!
The Natural Women's Health Guide, Volume 2 - Fertility, Natural Fertility Enhancers, Infertility Treatments, and Natural Libido Boosters - BUY HERE!

Related Posts:
Resources:
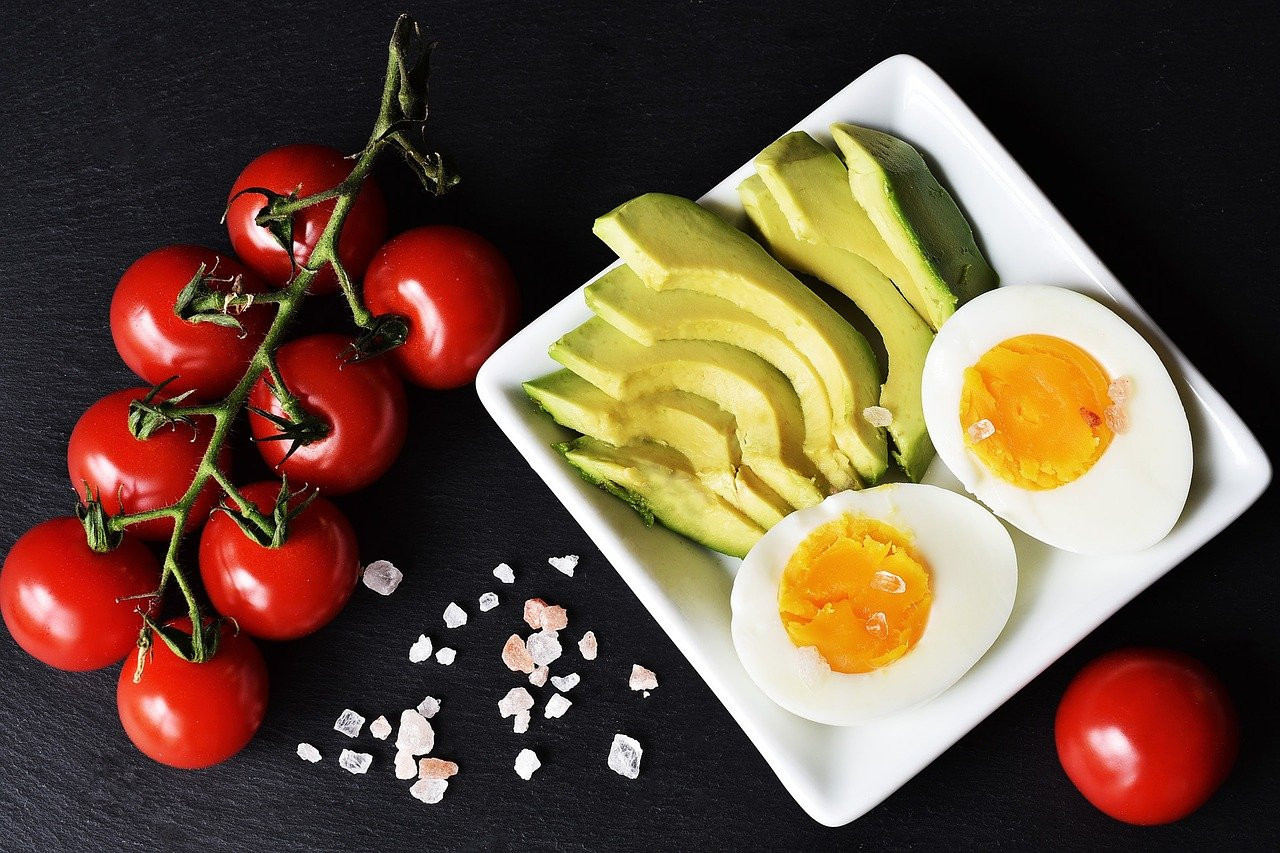
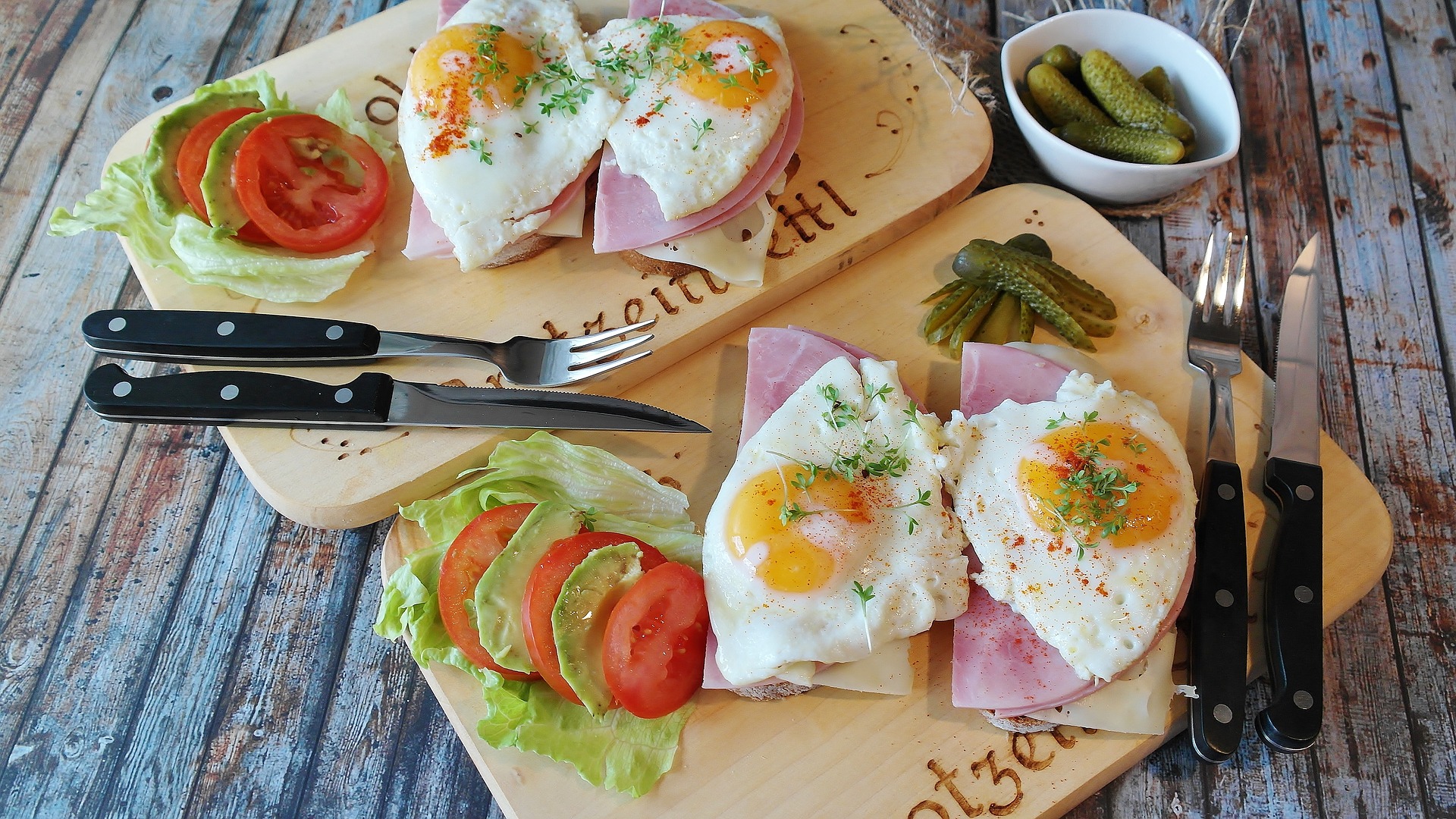
 The ketogenic diet is a high protein, high fat, low carbohydrate diet. Though fruits, vegetables, and grains ARE permitted, they are generally consumed in small quantities. Meanwhile, foods like meats, animal products, nuts, and other sources of fats and proteins are eaten in higher quantities in order to encourage the body to enter a state of ketosis (put simply, meaning that the body is using ketones as a sources of fuel rather than glucose).
The ketogenic diet is a high protein, high fat, low carbohydrate diet. Though fruits, vegetables, and grains ARE permitted, they are generally consumed in small quantities. Meanwhile, foods like meats, animal products, nuts, and other sources of fats and proteins are eaten in higher quantities in order to encourage the body to enter a state of ketosis (put simply, meaning that the body is using ketones as a sources of fuel rather than glucose).